The Small Business Reorganization Act makes Chapter 11 reorganizations more accessible to small businesses, including retailers. Effective February 19, 2020, Subchapter V was added to Chapter 11 of the Bankruptcy Code so that qualifying small businesses could avoid some of the costs and delays associated with traditional Chapter 11 bankruptcy and exit bankruptcy quicker and more efficiently.
Below are some of the basic differences and commonalities between Subchapter V and traditional Chapter 11 retail bankruptcy cases, followed by the eligibility requirements to file a Subchapter V bankruptcy case. In the next issue of Bankruptcy Basics, we’ll go into greater detail on the Subchapter V plan process, including more specific differences, such as the requirement that a tenant’s net disposable income be paid to creditors over the course of three to five years and the ability of a small business owner to retain equity even if creditors are not paid in full.
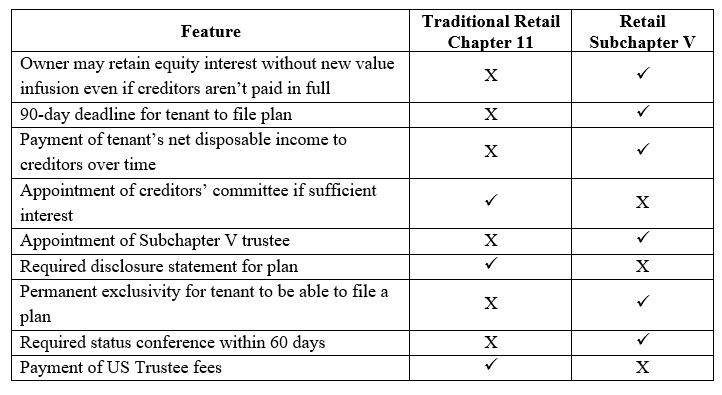
Differences Between Traditional Chapter 11 and Subchapter V Retail Bankruptcy Cases
Subchapter V retains many of the features of regular Chapter 11 cases, but it also differs in a number of ways, including:
 Commonalities Between Traditional Chapter 11 and Subchapter V Retail Bankruptcy Cases
Commonalities Between Traditional Chapter 11 and Subchapter V Retail Bankruptcy Cases
The following retail-related aspects of traditional Chapter 11 bankruptcy cases, among others, also apply in cases under Subchapter V:
- Tenant’s lease decision timing
- Currently 120 days from the filing date with a potential 90-day extension; formerly was 210 days from the filing date with a potential 90-day extension, which may still be the case for current tenants in Chapter 11 whose cases were filed before December 27, 2022
- Tenant’s lease assumption requirements
- Cure of defaults and showing of adequate assurance of future performance (with heightened shopping center standards) required for lease assumption or assumption/assignment
- Impact of automatic stay
- Creditors such as landlords are prevented from taking most actions related to collection or property without court approval
Retail Tenant Eligibility for Subchapter V Bankruptcy Filing
Under the initial eligibility rules of Subchapter V, a small business debtor was required to be an entity “engaged in commercial or business activities” that generated 50 percent or more of its debt from those activities with total noncontingent, liquidated debt (which may be secured, unsecured, or both) of no more than $2,725,625 owed to nonaffiliates or noninsiders.
Almost immediately after Subchapter V became effective, Congress passed the CARES Act in March 2020, under which the debt limit for Subchapter V eligibility was increased to $7.5 million owed to nonaffiliates or noninsiders through March 2021. This higher debt limit was again extended for one year in March 2021, and in June 2022, it was retroactively extended from March 2022 through June 2024 (the current expiration date). Given the continued, substantial use of Subchapter V, it is widely expected that the $7.5 million debt limit will be extended again, either temporarily or permanently.